Troubleshooting XMLRPC
If an XMLRPC synchronization attempt fails, a notice is generated in the GUI to bring attention to it, as seen in XMLRPC Sync Failure Notice. The notice typically contains some information about why it failed that points to a fix, but if that is not enough, check the other items in this section.
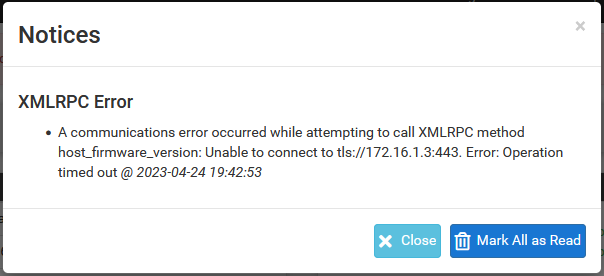
XMLRPC Sync Failure Notice
Check the System Log
XMLRPC failure details are logged to the main system log (Status > System Logs, General tab). Usually the error is stated plainly, for example an authentication failure would indicate that the password entered for the Admin user on the synchronization settings was incorrect. As shown in XMLRPC Sync Failure Log Entry a timeout happened during the synchronization attempt. In this example it was due to a missing firewall rule.

XMLRPC Sync Failure Log Entry
Check the Firewall Log
Visit Status > System Logs, Firewall tab on the secondary node. Check the log for entries failing to reach the secondary’s Sync interface on the GUI port, as seen in XMLRPC Sync Failure Firewall Log Entry. If the traffic is shown as blocked, adjust the Sync interface rules as needed.
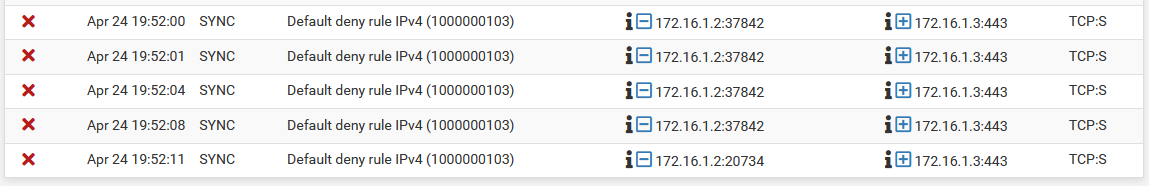
XMLRPC Sync Failure Firewall Log Entry
Check the Admin User
Visit System > User Manager and ensure that the admin user is enabled on both systems and that the admin password is the same on both systems. Visit System > High Avail Sync and double check that the admin username has been entered and that the correct password is present.
Verify Connectivity
Check Status > Interfaces and ensure the Sync interface shows a link on both units. If there is no link, ensure a cable is connected between the two units. The ports on the SG-4860 are Auto-MDIX so either a straight-through patch or a crossover cable will work. If a short cable is in use, try a longer cable (minimum 3ft/1m). If a link can still not be achieved, try using a small switch or VLAN between the two nodes.
Add a firewall rule to the Sync interface to allow ICMP echo requests and then attempt to ping from one firewall to the other to ensure they can reach each other at layer 3. If they cannot, double check the interface IP address and subnet mask settings, along with the cabling.
Troubleshooting pfsync
If the pfsync nodes do not line up under Status > CARP, that can indicate that the states have not been synchronized.
Check Firewall Rules
Check the firewall log at Status > System Logs, Firewall tab on both nodes. If any pfsync protocol traffic is present, the firewall rules on the Sync interface are probably incorrect.
Look at Firewall > Rules on the Sync interface tab. Make sure that the rules will pass pfsyncprotocol traffic, or traffic of any protocol, to any destination. Adjust the rules accordingly and check the logs and CARP status again to see if it starts working.
Verify Connectivity
See Verify Connectivity above to check the connection between the nodes.
Check Interfaces
If the states appear to sync but failover is still not seamless, check Interfaces > (Assign) and make sure the interfaces all line up physically as well as by name. In pfSense 2.2 and later, the states are bound to the interface so if, for example, the LAN interface is igb0 on one unit but igb3 on the other, then the states will not line up. Fix the interfaces so they are identical on both units.
Troubleshooting Local Services
DNS Resolution
If local clients are unable to obtain DNS responses from a CARP VIP on the cluster, check the following items:
- If using the default DNS Resolver (unbound), visit Services > DNS Resolver and click Save on the primary to ensure the default values are fully respected.
- If using either the DNS Resolver or DNS Forwarder, ensure the daemon is configured to listen on All interfaces or at least Localhost and the internal CARP VIPs.
- Ensure the local interface firewall rules pass both TCP and UDP port 53 to the CARP VIPs used for local DNS.
- Ensure the firewall itself has DNS servers configured under System > General, especially if using the DNS Forwarder (dnsmasq) instead of the DNS Resolver (unbound).
DHCP
If the DHCP failover pool status does not reach “normal”, there are a few items to check:
- Ensure both units are connected to the same switch/subnet on the correct interface.
- Verify connectivity between the two units on that interface.
- Ensure the failover peer IP address has been properly configured
- Ensure that there is a CARP VIP on the interface in question
- Ensure that the CARP VIP on the primary node has a skew of 0 or 1, and the secondary has a skew of 100 or higher.
- If all else fails:
- Click
 to stop the DHCP service from Status > Services on both nodes
to stop the DHCP service from Status > Services on both nodes - Visit Diagnostics > Command Prompt on both nodes
- Run the following command in the Shell Execute box on both nodes:
rm /var/dhcpd/var/db/dhcpd.leases* - Click
 to start the DHCP service from Status > Services on both nodes
to start the DHCP service from Status > Services on both nodes
- Click