The Essentials of SDWAN Architecture
SD-WAN Architecture for enterprises
Software-defined wide area networking (SD-WAN), provides the benefits of modern software-defined networking (SDN) technology to traditionally hardware-based networking. It is an overlay architecture providing a networking infrastructure that is much higher security and more easier to manage than legacy WANs, essentially moving the control layer (SDWAN controller or SDWAN gateway) to the internet — and in the process, centralizing and simplifying network management. This overlay design abstracts software from hardware, enabling network virtualization and making the network more elastic.
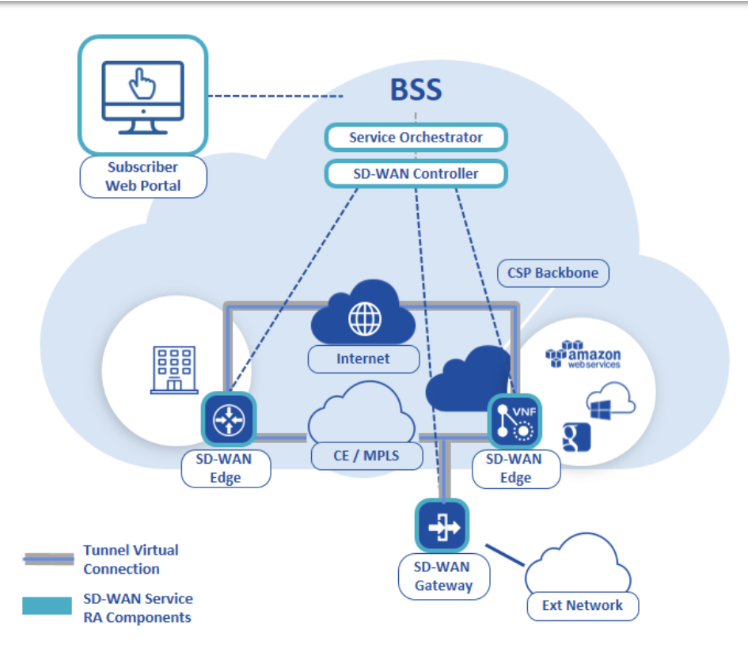
What Do Enterprises Need in an SD-WAN Architecture ?
Enterprises have been increasingly investing in the flexible cloud solutions or intra-company connection, and SD-WAN represents an effort to engineer similar benefits in their data center architecture. SD-WAN architecture is particularly beneficial to environments separated by distance — for example, between main offices and branch offices. Whereas traditional WAN can be expensive and complex, SD-WAN architecture reduces recurring network costs, offers network-wide control and visibility, and simplifies the technology with zero-touch deployment and centralized management. Key to the SD-WAN architecture is that it can communicate with all network endpoints without the need for external mechanisms or additional protocols.
The Importance of Security in SD-WAN
Aside from that array of SD-WAN benefits, arguably the primary advantage of an SD-WAN architecture is security.
Today’s companies prefer network architectures that integrate security, policy, and orchestration., and SD-WAN covers those bases by unifying secure connectivity. In the SD-WAN architecture, a company benefits from end-to-end encryption across the entire network, including the Internet. All devices and endpoints are completely authenticated as internal network, thanks to a scalable key-exchange functionality and software-defined security. All communication between the main office and branch offices is secured, as is communication to and from the cloud and work like an full time internal network. (i.e. 192.168.x.x ...)
The extra advantage SD-WAN is the Data Traffic Optimization
Aside from the all communication between the main office and branch offices is secured.
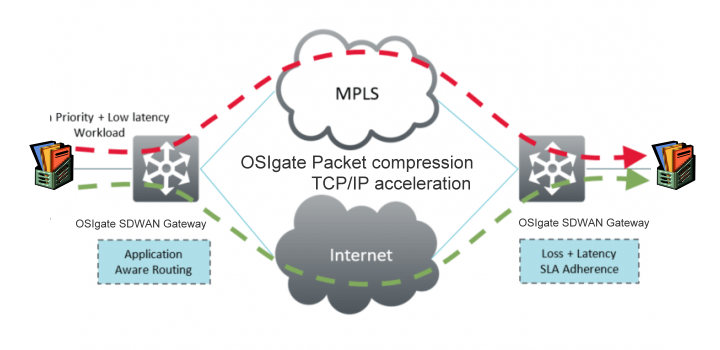
OSIgate SDWAN Optimizer (i.e. OSIgate 6000i) reduce bandwidth cost and Accelerate Internet application, 20%~200% speeds up internet after SDWAN Optimizer, by using Real Time Packet Compression, Packet Correction, Packets Deduplication, Packet cache , Software Define WAN (SDWAN, as similar as MPLS line or lease line). Gain Bandwidth from the SDWAN protocol via hardware level compression by Intel AES-NI (Advanced Encryption Standard New Instructions) instruction set.
Types of SD-WAN Architecture
SD-WAN providers offer several general types of SD-WAN architecture — namely, premises-based, MPLS-based, Router-based and Cloud-based.
Premises-based SD-WAN solutions (i.e. OSIgate SDWAN Optimizer, model 6000i) involve an appliance that is placed onsite to achieve SD-WAN functionality. Premises-based SD-WANs can be cost-effective solutions for smaller, localized businesses.
MPLS-based SD-WAN solutions involve multiple appliances (i.e. OSIgate SDWAN Router, OSIgate SDWAN Optimizer) placed at network endpoints. These solutions create a virtual IP network between the vendor-proprietary appliances, giving them control of network packets from end to end.
Internet-based SD-WAN solutions also use multiple VM/Cloud instance/SDWAN gateway at each customer location, using public Internet connections from customer-chosen providers. The customer pays for a portion of its Internet connections to be SD-WAN.
Each of these architecture types varies in cost and benefits, and might be more or less appropriate for a given environment. Regardless of the type, all of these solutions offer a full range of SD-WAN capabilities.
Updated April 2019 by Connor Craven
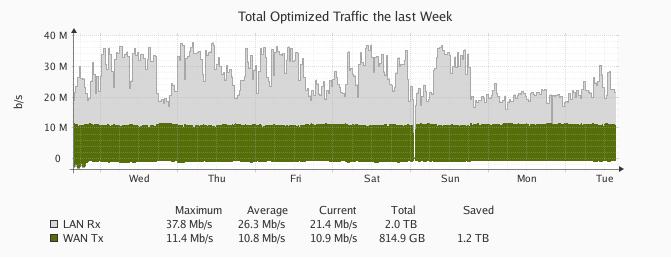
Replication approach 40 Mbps in LAN while the WAN just remains at 11 Mbps, resulting in 1.2 TB saved for the week. It is showing a 11Mbps data line but have 30~40Mbps performance in result.