Troubleshooting High Availability
In the event that any of the testing fails, there are a few common things to check.
Review the Configuration
Before digging too deep into the technical details below, first review the configuration and ensure all steps were followed accurately.
Troubleshooting CARP
Check Interface Status
If an interface shows “INIT” for the CARP state, as shown in CARP Status on Primary with Disconnected Interface, most commonly this indicates that the interface upon which this VIP resides is not connected to anything. If there is no link to a switch or another port, the interface is down and the VIP cannot be fully initialized. If the NIC is plugged in and appears to have a link when this occurs, edit, save, and apply changes for the VIP in question to reconfigure it.
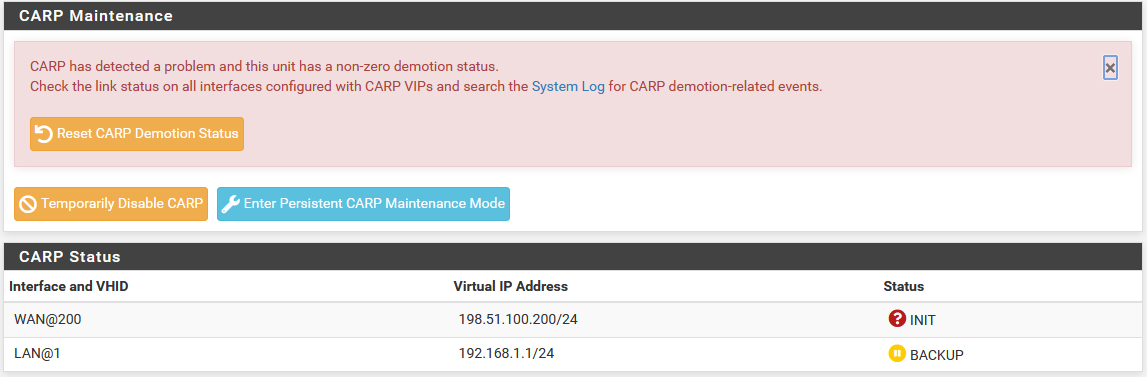
CARP Status on Primary with Disconnected Interface
Conflicting VHIDs
The VHID determines the virtual MAC address used by that CARP IP. The input validation in pfSense will not permit using conflicting VHIDs on a single pair of systems, however if there are multiple systems on the same broadcast domain running CARP, it is possible to create a conflict. VRRP also uses the same virtual MAC address scheme, so a VRRP IP using the same VRID as a CARP IP VHID will also generate the same MAC address conflict.
When using CARP on the WAN interface, this also means VRRP or CARP used by the ISP can also conflict. Be sure to use VHIDs that are not in use by the ISP on that broadcast domain.
In addition to creating a MAC conflict which can interfere with traffic, it can also interfere with the CARP VIP status.
Incorrect Subnet Mask
The subnet mask for a CARP VIP must match the subnet mask on the Interface IP address for the same subnet. For example, if an interface IP address is 192.168.1.2/24, the CARP VIP must also be 192.168.1.1/24.
Switch/Layer 2 Issues
Typically a switch or layer 2 issue manifests itself as both units showing “MASTER” status for one or more CARP VIPs. If this happens, check the following items:
- Ensure that the interfaces on both boxes (The WANs, LANs, etc, etc) are connected to the proper switch/VLAN/layer 2. For example, ensure that the LAN port on both units is connected to the same switch/VLAN.
- Verify that the two nodes can reach each other (via ICMP echo, for example) on each segment. Firewall rules may need to be added to WAN to accommodate this test.
- If the units are plugged into separate switches, ensure that the switches are properly trunking and passing broadcast/multicast traffic.
- If the switch on the back of a modem/CPE is being used, try a real switch instead. These built-in switches often do not properly handle CARP traffic. Often plugging the firewalls into a proper switch and then uplinking to the CPE will eliminate problems.
- Disable IGMP snooping or other multicast limiting and inspecting features. If they are already off, try enabling the feature and disabling it again.