Configuring a HA Cluster
Note
The WAN and LAN should be configured to static addresses prior to configuring a HA Cluster. Please see High Availability Prerequisites for IP address details.
This is the heart of the process, making the changes that will link the systems and allow them to function together.
Setup Sync Interface
Before proceeding, the Sync interfaces on the cluster nodes must be configured. Sync IP Address Assignments lists the addresses to use for the Sync interfaces on each node.
- Navigate to Interfaces and choose the interface to use on the SYNC port
- Check Enable Interface
- Enter
SYNCfor the Description - Set IPv4 Configuration Type to Static IPv4
- Set IPv4 address to
172.16.1.2when configuring the primary node, or172.16.1.3when configuring the secondary node - Select 24 for the subnet mask in the CIDR drop-down next to IPv4 address
- Do not check Block private networks or Block bogon networks
- Click Save
- Click Apply Changes
Once that procedure has been completed on the primary node, perform it again on the secondary node with the appropriate IPv4 address value. Remember they must be the same on both nodes.
After configuring the sync interface, the interface assignments should have one labeled SYNC.
Add Firewall Rules for Synchronization
To complete the Sync interface configuration, firewall rules must be added to both nodes to allow synchronization.
At a minimum, the firewall rules must pass the configuration synchronization traffic (by default, HTTPS on port 443) and pfsync traffic. In most cases, a simple “allow all” style rule is used. For this guide, both will be shown and it will also serve as an indicator that synchronization is working.
On the primary node:
Set up a rule to allow configuration synchronization:
- Navigate to Firewall > Rules on the SYNC tab
- Click
 at the top of the list to create a new rule
at the top of the list to create a new rule - Set Action to Pass
- Set Source to SYNC Net
- Set Destination to SYNC Address
- Set Destination port range to
443or choose HTTPS (443) from the drop-down selector - Set Description to
Allow configuration synchronization - Click Save
Set up a rule to allow state synchronization:
- Click
 at the top of the list to create another new rule
at the top of the list to create another new rule - Set Action to Pass
- Set Protocol to pfsync
- Set Source to SYNC Net
- Set Destination to any
- Set Description to
Allow state synchronization - Click Save
Set up a rule to allow ICMP echo (ping) for Diagnostics:
- Click
 at the top of the list to create another new rule
at the top of the list to create another new rule - Set Action to Pass
- Set Protocol to ICMP
- Set Source to SYNC Net
- Set Destination to SYNC Net
- Set Description to
Allow ICMP echo (ping) for Diagnostics - Click Save
- Click Apply Changes
When complete, the rules will look like the following, which also includes a rule to allow ICMP echo (ping) for diagnostic purposes.
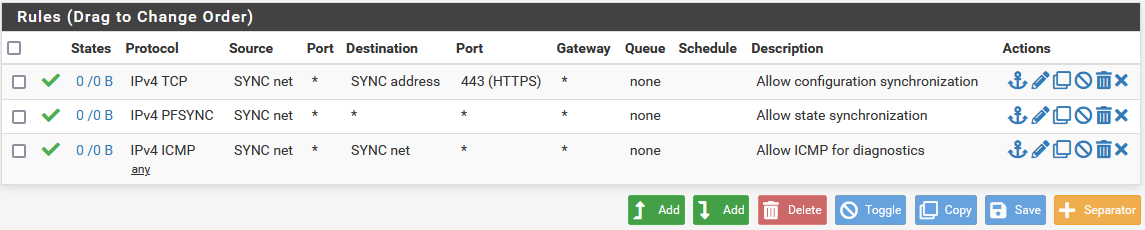
Example Sync Interface Firewall Rules
On the secondary node:
- Navigate to Firewall > Rules on the SYNC tab
- Click
 at the top of the list to create a new rule
at the top of the list to create a new rule - Set Action to Pass
- Set Protocol to any
- Set Source to SYNC Net
- Set Destination to any
- Set Description to
Temp rule for sync - Click Save
- Click Apply Changes
Note
The rule on the secondary is different, but that is intended at this point. Once the first configuration synchronization has taken place, the temporary rule on the secondary will be replaced by the rules from the primary. Seeing that the rules on the Sync interface changed is a good indicator that it worked!
Configure pfsync
State synchronization using pfsync must be configured on both the primary and secondary nodes to function.
First on the primary node and then on the secondary, perform the following:
- Navigate to System > High Avail. Sync
- Check Synchronize States
- Set Synchronize Interface to SYNC
- Set pfsync Synchronize Peer IP to the other node. Set this to
172.16.1.3when configuring the primary node, or172.16.1.2when configuring the secondary node - Click Save
Configure XMLRPC
Warning
Configuration synchronization must only be configured on the primary node. Never activate options in this section on the secondary node of a two-member cluster.
On the primary node only, perform the following:
-
Navigate to System > High Avail. Sync
-
Set Synchronize Config to IP to the secondary node’s Sync interface IP address,
172.16.1.3 -
Set Remote System Username to
admin.Note
This must always be
admin. No other user will work! -
Set Remote System Password to the admin user account password and be sure to confirm the password.
-
Check the boxes for each area to synchronize to the secondary node. For this guide, as with most configurations, all boxes are checked.
-
Click Save
As a quick confirmation that the synchronization worked, on the secondary node navigate to Firewall > Rules on the SYNC tab. The rules entered on the primary are now there, and the temporary rule is gone.
The two nodes are now linked for configuration synchronization! Changes made to the primary node in supported areas will be synchronized to the secondary whenever a change is made.
Warning
Do not make changes to the secondary in areas set to be synchronized! These changes will be overwritten the next time the primary node performs a synchronization.
Add CARP VIPs
Now that the configuration synchronization is complete, the CARP Virtual IP addresses need only be added to the primary node and they will be automatically copied to the secondary. For this demonstration, two CARP VIPs will be added: One for WAN, and one for LAN.
-
Navigate to Firewall > Virtual IPs on the primary node.
-
Click
 at the top of the list to create a new VIP
at the top of the list to create a new VIP -
Set Type to CARP
-
Set Interface to WAN
-
Enter the WAN CARP VIP into the IP Address(es) section Address box and pick the appropriate subnet mask. For this example, enter
198.51.100.200and24(See WAN IP Address Assignments). -
Enter a random password in Virtual IP Password. This need only match between the two nodes, which will be handled by synchronization.
-
Select an unused VHID Group as determined in Determine CARP VHID Availability.
Note
A common tactic is to make the VHID match the last octet of the IP address, so in this case
200would be chosen. -
Set the Advertising Frequency to a Base of 1 and a Skew of 0. This value will be automatically adjusted when it is copied to the secondary.
-
Enter a Description such as
WAN CARP VIP. -
Click Save
-
Click Apply Changes
The Base and Skew together determine how often a CARP heartbeat is sent. The value of Baseadds whole seconds and should match between the two nodes. The Skew value adds 1/256th of a second increments. The primary node should always have a Skew of 0 or 1. The secondary node must be higher, typically 100+. That adjustment is handled automatically by the configuration synchronization process.
Note
If CARP appears to be too sensitive to latency on a given network, adjusting the Base by adding one second at a time is recommended until stability is achieved.
Repeat the above process for the LAN CARP VIP:
- Navigate to Firewall > Virtual IPs
- Click
 at the top of the list to create a new VIP
at the top of the list to create a new VIP - Set Type to CARP
- Set Interface to LAN
- Enter the LAN CARP VIP into the IP Address(es) section Address box and pick the appropriate subnet mask. For this example, enter
192.168.1.1and24(See LAN IP Address Assignments). - Enter a random password in Virtual IP Password.
- Select an unused VHID Group as determined in Determine CARP VHID Availability.
- Set the Advertising Frequency to a Base of 1 and a Skew of 0.
- Enter a Description such as
LAN CARP VIP. - Click Save
- Click Apply Changes
If there are any additional IP addresses in the WAN subnet that will be used for purposes such as 1:1 NAT, port forwards, VPNs, etc, they may be added now as well.
Check Firewall > Virtual IPs on the secondary node to ensure that the VIPs synchronized as expected.
The Virtual IP addresses on both nodes will look like the following if the process was successful.
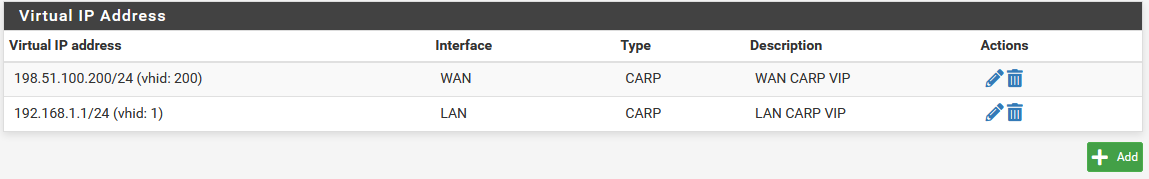
CARP Virtual IP Address List
Check CARP Status
Now visit Status > CARP on both nodes to confirm the proper status. The primary node should indicate MASTER status for all VIPs, and the secondary node should indicate BACKUP status for all VIPs. If the status is incorrect, see Troubleshooting High Availability.
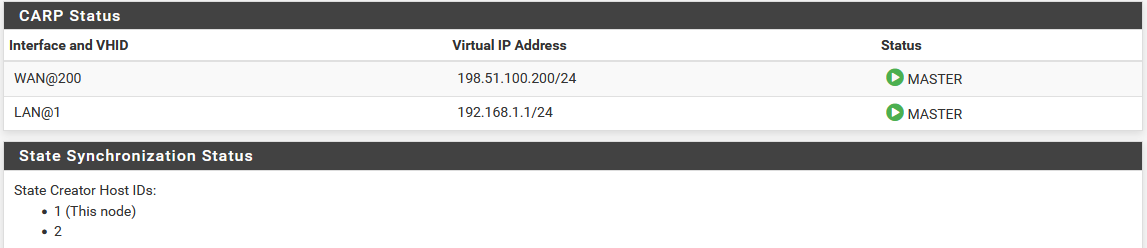
CARP VIP Status on Primary
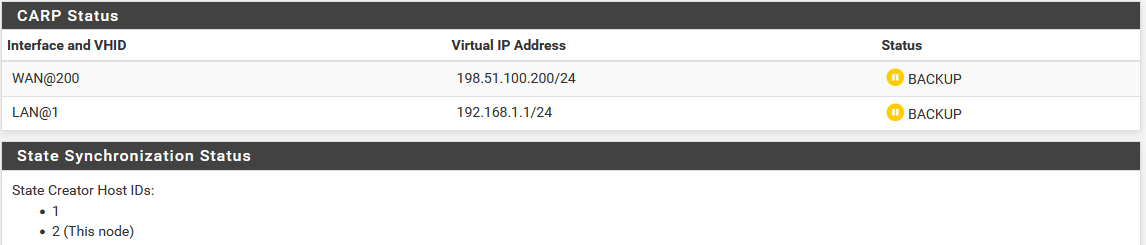
CARP VIP Status on Secondary
Setup Manual Outbound NAT
Now it is time to put the new CARP VIPs to use. The NAT settings will synchronize so these changes need only be made to the primary node.
-
Navigate to Firewall > NAT, Outbound tab on the primary node
-
Change the Mode to Manual Outbound NAT rule generation
-
Click Save, the rule list will be populated with rules equivalent to what was in use for the default, Automatic Outbound NAT.
Note
If no rules appear in the list, ensure the WAN has a gateway selected under Interfaces > WAN
-
Click
 to edit the rule for the LAN subnet
to edit the rule for the LAN subnet -
Set Translation to the WAN CARP VIP, 198.51.100.200 in this example.
-
Click Save
-
Repeat that edit for each rule in the list except the rules with a source of 127.0.0.0/8.
-
Click Apply Changes
-
Visit Firewall > NAT, Outbound tab on the secondary node to ensure the rule changes are reflected there.
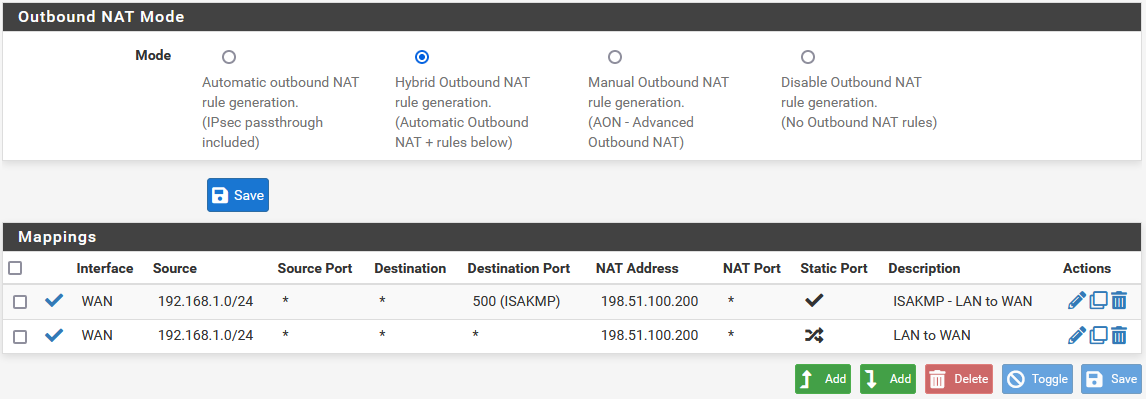
Outbound NAT Rules for LAN with CARP VIP
Warning
If additional local interfaces are added later, such as a second LAN, DMZ, etc, and that interface uses private IP addresses, then additional manual outbound NAT rules must be added at that time.
Other NAT Concerns
If there are any port forwards to be added using the WAN CARP VIP, they may be added now using Firewall > NAT, Port Forward tab. Port forwards will work the same as usual, but the Destinationwill be the WAN CARP VIP.
Setup DHCP
The DHCP server daemons on the cluster nodes need adjustments so that they can work together. The changes will synchronize from the primary to the secondary, so as with the VIPs and Outbound NAT, these changes need only be made on the primary node.
- Navigate to Services > DHCP Server, LAN* tab.
- Set the DNS Server to the LAN CARP VIP, here
192.168.1.1 - Set the Gateway to the LAN CARP VIP, here
192.168.1.1 - Set the Failover Peer IP to the actual LAN IP address of the secondary node, here
192.168.1.3 - Click Save
Setting the DNS Server and Gateway to a CARP VIP ensures that the local clients are talking to the failover address and not directly to either node. This way if the primary fails, the local clients will continue talking to the secondary node.
The Failover Peer IP allows the daemon to communicate with the peer directly in this subnet to exchange data such as lease information. When the settings synchronize to the secondary, this value is adjusted automatically so the secondary points back to the primary.
On both nodes, visit Status > DHCP Leases to see the status. A section will be displayed at the top containing the failover pool status, one line will be shown for each local interface pool. When the two nodes are working properly, both will indicate a “normal” status.

DHCP Failover Status
VPNs and Other Services
When configuring a VPN, such as OpenVPN or IPsec, pick a WAN CARP VIP as the Interface for the VPN and ensure the remote peer also builds the other side of the tunnel using the CARP VIP as the peer address.
For other local services, packages, etc. likewise a CARP VIP is recommended for binding if the service will work on both nodes.
High Availability support in packages varies. Check the package documentation for information on if, or how, various aspects of High Availability work with a specific package.
Additional Interfaces
Additional local interfaces may also be configured, repeating some of the previous steps as needed:
- Assign the interface on both nodes identically
- Enable the interface on both nodes, using different IP addresses within the same subnet
- Add a CARP VIP inside the new subnet (Primary node only)
- Add firewall rules (Primary node only)
- Add Manual Outbound NAT for a source of the new subnet, utilizing the CARP VIP for translation (Primary node only)
- Configure the DHCP server for the new subnet, utilizing the CARP VIP for DNS and Gateway roles (Optional, Primary node only)
