Components of a High Availability Cluster
Though often erroneously called a “CARP Cluster”, two or more redundant pfSense firewalls are more aptly titled a “High Availability Cluster”, since CARP is only one of several technologies used to achieve High Availability with pfSense.
The most common High Availability cluster configuration includes only two nodes. It is possible to have more nodes in a cluster, but they do not provide a significant advantage. This guide assumes two SG-4860 nodes are in use, one acting as the primary node and the other as the secondary node.
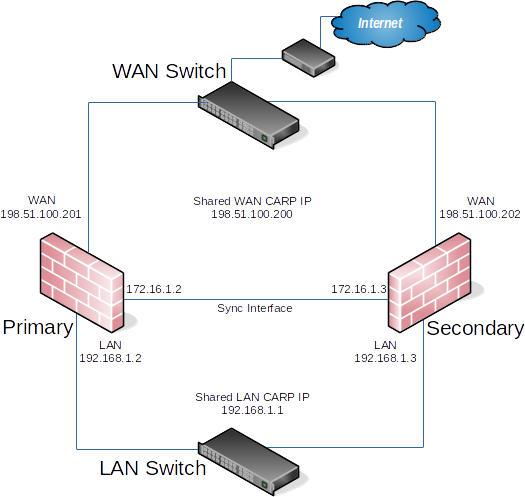
Example High Availability Cluster
IP Address Redundancy (CARP)
For connectivity through a cluster to continue seamlessly during failover, traffic to and from the cluster must use redundant IP addresses. In pfSense, Common Address Redundancy Protocol (CARP) is used for this task.
A CARP type Virtual IP address (VIP) is shared between nodes of a cluster. One node is master and receives traffic for the IP address, and the other nodes maintain backup status and monitor for heartbeats to see if they need to assume the master role if the previous master fails. Since only one member of the cluster at a time is using the IP address, there is no IP address conflict for CARP VIPs.
In order for failover to work properly it is important that inbound traffic coming to the cluster (routed upstream traffic, VPNs, NAT, local client gateway, DNS requests, etc) be sent to a CARP VIP and for outgoing traffic such as Outbound NAT to be sent from a CARP VIP. If traffic is addressed to a node directly and not a CARP VIP, then that traffic will not be picked up by other nodes.
CARP works similar to VRRP and HSRP, and may even conflict in some cases. Heartbeats are sent out on each interface containing a CARP VIP, one heartbeat per VIP per interface. At the default values for skew and base, a VIP sends out heartbeats about once per second. The skew determines which node is master at a given point in time. Whichever node transmits heartbeats the fastest assumes the master role. A higher skew value causes heartbeats to be transmitted with more delay, so a node with a lower skew will be the master unless a network or other issue causes the heartbeats to be delayed or lost.
Note
Never access the firewall GUI, SSH, or other management mechanism using a CARP VIP. For management purposes, only use the actual IP address on the interface and not the VIP. Otherwise it cannot be determined beforehand which unit is being accessed.
Configuration Synchronization (XMLRPC)
To make the job of maintaining two practically identical firewall nodes easier, configuration synchronization is possible using XMLRPC. Some areas cannot be synchronized, such as the Interface configuration, but many other areas can: Firewall rules, aliases, users, certificates, VPNs, DHCP, routes, gateways, and more. As a general rule, items specific to hardware or a particular installation, such as Interfaces or values under System > General or System > Advanced do not synchronize. For a list of areas that will synchronize, see the checkbox items on System > High Avail Sync in the XMLRPC section. Most packages will not synchronize but some contain their own synchronization settings. Consult package documentation for more details.
When XMLRPC Synchronization is enabled, settings from supported areas are copied to the secondary and activated after each configuration change.
XMLRPC Synchronization is optional, but maintaining a cluster is a lot more work without it.
State Table Synchronization (pfsync)
Active connection state information is exchanged between nodes using the pfsync protocol to achieve seamless failover. When pfsync is active and properly configured, all nodes will have knowledge of each connection flowing through the cluster. If the master node fails, the backup node will take over and clients will not notice the transition since both nodes knew about the connection beforehand.
Failover can still operate without pfsync, but it will not be seamless. Without pfsync if a node fails and another takes over, user connections would be dropped. Users may immediately reconnect through the other node, but they would be disrupted during the transition.